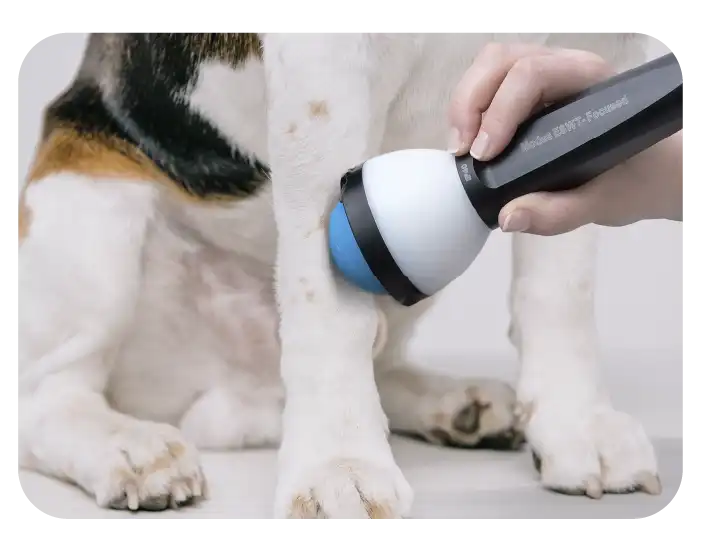
FOCUSED ESWT FEATURES
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive method and is widely used for various musculoskeletal diseases as well as in urology. There are 3 mechanisms for generating shock waves: electrohydraulic, electromagnetic, and piezoelectric.
Electrohydraulic devices generate shock waves through a discharge in a fluid medium due to the high voltage applied to the tips of the electrodes. This shock wave is focused with the help of a reflector. [1]
Electromagnetic shock wave devices operate on the principle of inducing a magnetic field and the shock wave is focused using acoustic lenses.
Piezoelectric ESWT devices, on the other hand, place a large number of piezo crystals inside a sphere, and a rapid electrical discharge is provided. As the crystals contract and expand, a pressure builds up in the water, and a shock wave is produced. Focusing is determined by arranging the crystals in different geometries within the sphere.
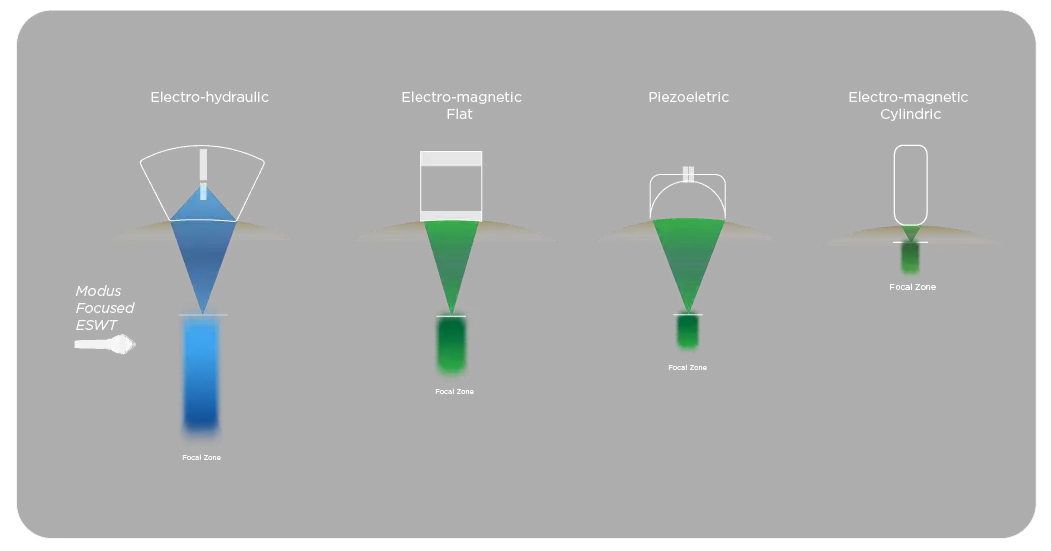 Figure 1. Different ESWT Device Mechanisms Used in Pressure and Shock Wave Production [2]
Figure 1. Different ESWT Device Mechanisms Used in Pressure and Shock Wave Production [2]
COMPARISON OF ESWT DEVICES
Waveform Characteristics
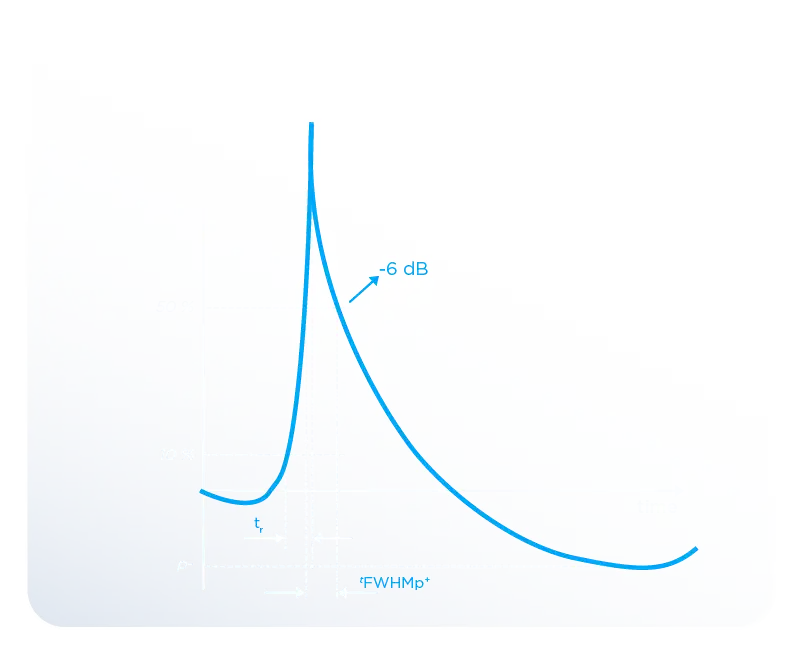
Electrohydraulic devices produce shock waves with shorter rise times than piezoelectric and electromagnetic devices. The rise time of electrohydraulic devices has been measured at approximately 35 ns, while the rise time of the Modus Focused ESWT device is 31 ns. This allows for faster energy transfer to the targeted area and less signal distortion as it reaches the target. In piezoelectric and electromagnetic devices, since the rise time is longer, more oscillations and distortions are observed in the waves they produce.
This situation can cause the shock wave to reach the treatment area later and with reduced effectiveness. For these reasons, the short rise time in electrohydraulic devices ensures effective treatment in the desired area during shock wave therapy application. [3]
 Figure 2. Pressure-Time Graph obtained from Hydrophone Measurements of an Electrohydraulic Modus Focused ESWT Device
Figure 2. Pressure-Time Graph obtained from Hydrophone Measurements of an Electrohydraulic Modus Focused ESWT Device
Figure 3. Comparison of Rise Time for Three Different ESWT Devices,
EH (Electrohydraulic), EM (Electromagnetic), PE (Piezoelectric)
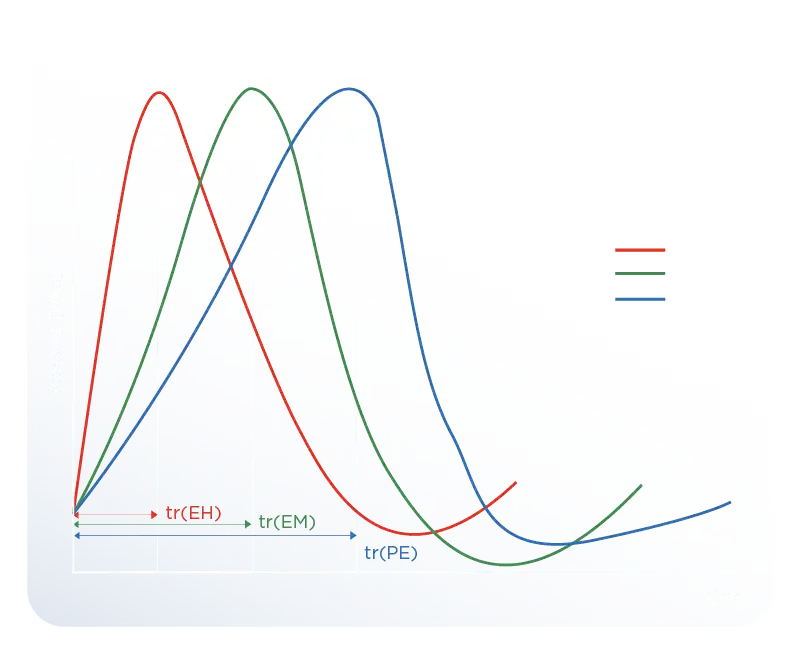 Figure 3. Comparison of Rise Time for Three Different ESWT Devices,
Figure 3. Comparison of Rise Time for Three Different ESWT Devices,
EH (Electrohydraulic), EM(Electromagnetic), PE(Piezoelectric)
Penetration Depth
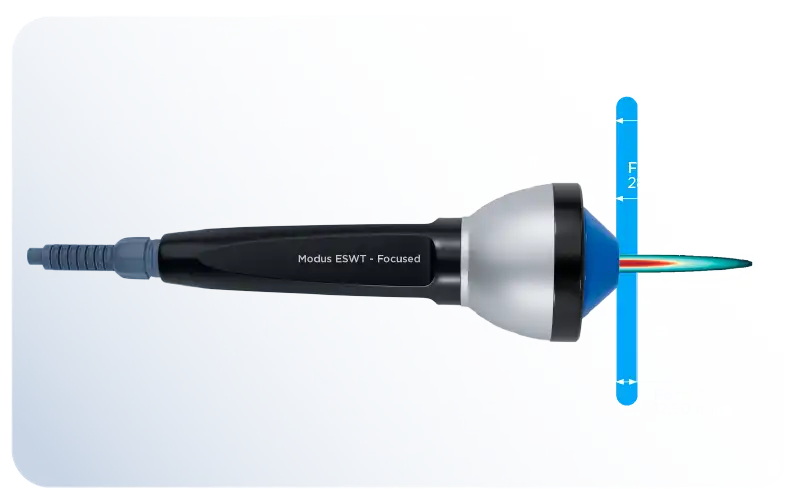
The penetration depth of piezoelectric shock waves is generally up to 5 cm and is the device that reaches the lowest treatment depth. The penetration depth of electromagnetic shock waves is around 6 cm, providing a more effective treatment depth than piezoelectric devices [4]. While the penetration depth is higher in electrohydraulic shock wave devices, the maximum penetration depth in the Modus Focused ESWT device can reach up to 8.45 cm. This creates an advantage for both superficial and deep treatments.
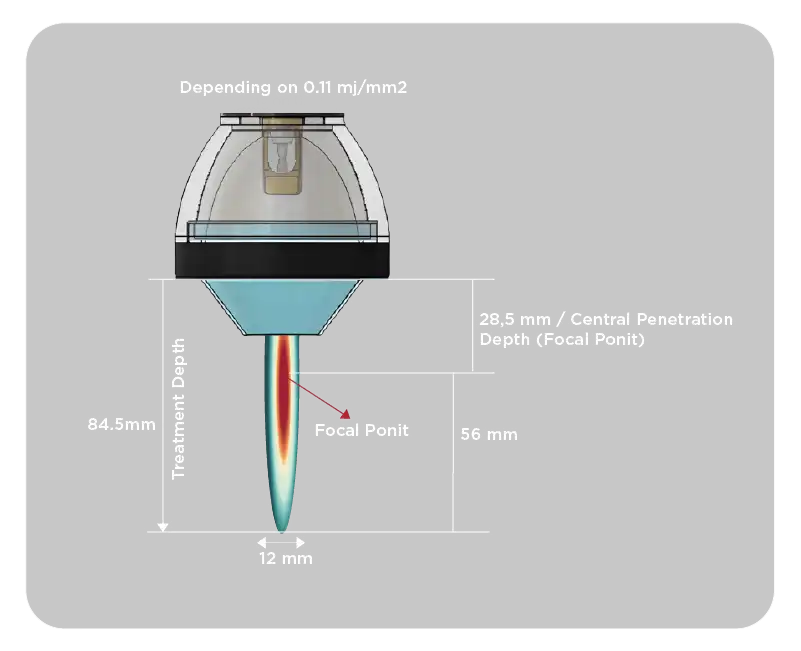 Figure 4. Representation of Penetration Depth for the Modus Focused ESWT Device
Figure 4. Representation of Penetration Depth for the Modus Focused ESWT Device
Treatment Area
Piezoelectric devices have the smallest focal volume, which can make it difficult to target the exact area. Although electromagnetic type devices affect a wider treatment area than piezoelectric devices, they do not have as large a treatment volume as electrohydraulic devices. Electrohydraulic devices are the ones that reach the highest area in the -6 dB focal region. The high energy and strong focusing capability of electrohydraulic technology make it possible to apply treatment to larger areas [5]. Since it has a large focal volume, it has been observed that it provides more energy transfer to the treated area for a specific energy flux density (mJ/mm2), thus shortening the treatment time.
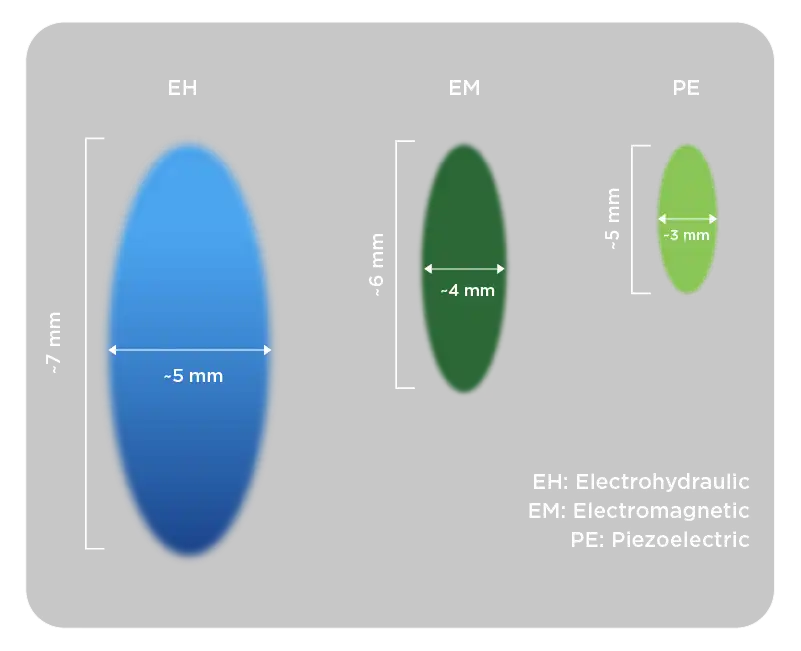 Figure 5: Representation of Focal Width and Treatment Depth for EH, EM, and PE ESWT Devices
Figure 5: Representation of Focal Width and Treatment Depth for EH, EM, and PE ESWT Devices
[1] [3] [6] Gladys L.Y. Cheing, Hua Chang. :Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy, Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 2003
[2] Vinzenz Auersperg, Klemens Trieb.: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: an update, EFORT Open Reviews, 2020
[4] Saxena, A. and Shou, L., 2019. Combined ESWT & RSW Therapy for Achilles Tendinopathy: A Prospective Study. Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons Journal (MLTJ), 9(4).